About the Division
The department of Chemistry is housed in the Lab Block of NCRMI and carries out R&D studies. It provides support to the development of projects, products or techniques/technology of the institute through experiment & trial investigations by espousing environmentally respectable processing techniques.
The department is equipped with Testing Laboratory to continually monitor the quality of coir fibre, coir pith and related products. The testing lab offers selected testing services to external customers in the areas of physical-chemical characterisation of coir fibre and coir pith-related products. The department is underway with major projects to develop technologies functional to industries as well as societies.
COCOAURA – Fragrance, Nature’s Way
COCOAURA, an organic car freshener, was developed as a natural alternative to traditional chemical air fresheners. It is meticulously crafted from coir pith and fibre, natural materials sourced from coconut husk, and provides a safe, chemical-free way to energise interior areas. Even after the product's usable life expires, the used coir pith and fibre may find a second life enhancing gardening soil. The product is incredibly eco-friendly and produces no waste during manufacture. COCOAURA has antibacterial and antifungal properties in addition to controlled release diffusion capabilities. There are five different ways to get COCOAURA: granulates, fibres, gel, sachets, and vent clips.
Development of chemical and biological system to treat ret liquor
In the process of coir fiber extraction from coconut husks, the traditional method of retting, involving soaking the husks in water, is time-consuming and generates retted water as a by-product. Discharging this water improperly can lead to pollution. Mechanical extraction of coir fiber is a quicker alternative, but it results in bright-colored fiber that can oxidize and become brown and coarse. Soaking the fiber for 24 hours after defibring helps reduce lightfastness and improves texture. The washed water from this process, known as ret liquor, is brown due to the organic matter present and can be harmful if released into water bodies.
The study also explores the use of biological treatment using fermenters. A double-chambered fermenter design showed a reduction in BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) of ret liquor. The system employs a mixture of cow dung slurry, cheese whey, and effluent from the paper industry as a source of bio-inoculum for anaerobic digestion of coir ret effluent, followed by filtration through coconut shell pieces. This treatment method holds promise for further analysis and standardization of inoculum sources and treated water quality.


Treatment of coir fibre with various biological and chemical agents to improve the texture and colour.
This study focuses a combined treatment (chemical and biological), that have a great potential to produce more consistent quality fibres with substantially reduced retting time and is more environmental friendly. To improve the coir fibre texture, trial experiments were conducted with a chemical softener developed by NCRMI.

Value addition of coir ret liquor with chemical methods
Soaking coconut husk in brackish water system for 6- 12 months is an old traditional practice carried out for the extraction of coir fibre from coconut husk. As a result of retting large quantities of organic substances including pectin, pentosan, fat, tannins, and also toxic phenols are liberated into water. All these processes contribute to pollution of water and air. This is reported to have devastating effect on the flora and fauna. This study focuses a combined chemical and biological methods should be environment friendly and economically viable treatment on ret liquor collected from various coir spinning societies.
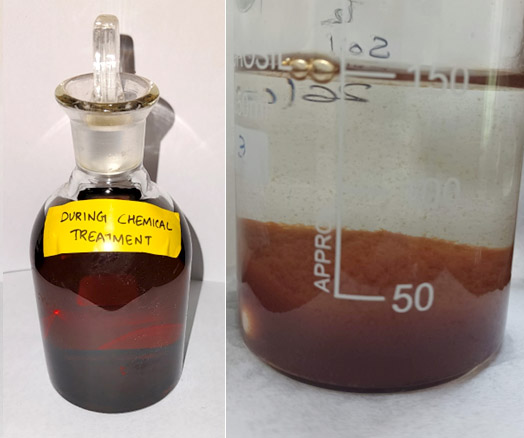



Development of biofilm on coir based biomass carriers for treating effluent water
The golden theme of our project is to recycle the waste water effluent in a path of a sustainable way by using microbial biofilms of coir based products. There are many chemical and mechanical processes to carry over the treatment of waste water for reusing. This chemical process paves a way for an unhealthy environment. Coir is a hard and tough organic fibre which possesses high specific area and wetting ability makes use as a suitable substrate for biofilm complex aggregation of microorganisms on fixed film processes. The main attraction of the project is that, this treatment system can be easily portable to any conditions and economically viable. The research is under progression with different products.
Infrastructure facility division of polymer chemistry
NCRMI has highly sophisticated Chemical laboratory offers advanced resources for specialised chemical examination of coir pith, fibre, and associated products. These tests provide information about the quality, purity, and suitability of coir for different applications. Testing of coir and coir-related products was done in accordance with IS standards.
 Kjeldahl acid digestion
Kjeldahl acid digestion
Kjeldahl acid digestion is a commonly used method in analytical chemistry for the decomposition and digestion of organic compounds containing nitrogen.
 Automated distillation system for the estimation of nitrogen and titration system
Automated distillation system for the estimation of nitrogen and titration system
An automated distillation system for nitrogen estimation is used to separate and quantify nitrogen compounds in a sample.
 Automatic fibre estimation system- for the determination of crude fibre, NDF, ADF, ADL, Cellulose, Hemicellulose. Lignin in plant materials, compound feed and food etc.
Automatic fibre estimation system- for the determination of crude fibre, NDF, ADF, ADL, Cellulose, Hemicellulose. Lignin in plant materials, compound feed and food etc.
An automatic fiber estimation system is a specialized instrument used for the determination of various fiber components in plant materials, compound feed, and food samples.
 Cold extraction system for defatting of fibre
Cold extraction system for defatting of fibre
Coir pith/ fiber may contain natural extractives, such as oils, resins, or tannins, which can impact its suitability for certain uses.
 pH system
pH system
The pH level of coir pith is an important parameter, especially when it is used as a growing medium.
 Bench conductivity /TDS/Salinity/Temp. Meter
Bench conductivity /TDS/Salinity/Temp. Meter
Conductivity measurements are useful for assessing the quality and purity of coir pith, particularly in relation to its salt content or the presence of other dissolved substances.
 Flame photometer
Flame photometer
The flame photometer is primarily used for the analysis of alkali and alkaline earth metals, such as sodium (Na), potassium (K), lithium (Li), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg present in the coir pith/fibre sample).
 UV-Spectrophotometer
UV-Spectrophotometer
A UV-visible spectrophotometer is a versatile analytical instrument that can be used to determine the chemical composition of elements in coir pith/fibre.
 Muffle furnace and Hot air oven
Muffle furnace and Hot air oven
Muffle furnace and Hot air oven are essential tools for preparing coir pith/fibre samples for subsequent analysis, such as determining the mineral content, moisture content, or other specific components of interest.
 Rotary Shaker
Rotary Shaker
A rotary shaker is a laboratory instrument used for the agitation and mixing of samples in various chemical and biological applications.
Training of coir pith composting and house holding composting to KCCPL : A seminar on the chemical characteristics of coir pith
A seminar was conducted to provide training on coir pith composting and household composting to KCCPL. The focus of the seminar was on imparting knowledge about the chemical characteristics of coir pith, a byproduct of the coconut industry. Participants were educated on effective methods for composting coir pith, emphasizing its eco-friendly nature. The training covered key aspects of composting, including understanding the chemical composition of coir pith, optimizing conditions for microbial activity, and ensuring proper household composting practices. This initiative aimed to enhance environmental sustainability, promote waste reduction, and empower individuals at KCCPL with the skills needed for efficient and responsible composting.
Training on health and safety measures in chemical handling for coir workers of various CVCS in connection with training on frame mats to coir societies conducted by NCRMI
The training program focused on enhancing awareness and understanding of health and safety protocols associated with the handling of chemicals during the processes of bleaching and dyeing of coir fibers, specifically to produce frame mats. The sessions aimed to equip coir workers with the necessary knowledge and skills to ensure a safe working environment while maintaining the quality standards of coir products.
- Sri Abhishek C, Scientist S3
- Smt Swathy Krishna V S, Technical Officer (Polymer Chemistry)
COCOAURA – Fragrance, Nature’s Way
COCOAURA, an organic car freshener, was developed as a natural alternative to traditional chemical air fresheners. It is meticulously crafted from coir pith and fibre, natural materials sourced from coconut husk, and provides a safe, chemical-free way to energise interior areas. Even after the product's usable life expires, the used coir pith and fibre may find a second life enhancing gardening soil. The product is incredibly eco-friendly and produces no waste during manufacture. COCOAURA has antibacterial and antifungal properties in addition to controlled release diffusion capabilities. There are five different ways to get COCOAURA: granulates, fibres, gel, sachets, and vent clips.
Development of chemical and biological system to treat ret liquor
In the process of coir fiber extraction from coconut husks, the traditional method of retting, involving soaking the husks in water, is time-consuming and generates retted water as a by-product. Discharging this water improperly can lead to pollution. Mechanical extraction of coir fiber is a quicker alternative, but it results in bright-colored fiber that can oxidize and become brown and coarse. Soaking the fiber for 24 hours after defibring helps reduce lightfastness and improves texture. The washed water from this process, known as ret liquor, is brown due to the organic matter present and can be harmful if released into water bodies.
The study also explores the use of biological treatment using fermenters. A double-chambered fermenter design showed a reduction in BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) of ret liquor. The system employs a mixture of cow dung slurry, cheese whey, and effluent from the paper industry as a source of bio-inoculum for anaerobic digestion of coir ret effluent, followed by filtration through coconut shell pieces. This treatment method holds promise for further analysis and standardization of inoculum sources and treated water quality.


Treatment of coir fibre with various biological and chemical agents to improve the texture and colour.
This study focuses a combined treatment (chemical and biological), that have a great potential to produce more consistent quality fibres with substantially reduced retting time and is more environmental friendly. To improve the coir fibre texture, trial experiments were conducted with a chemical softener developed by NCRMI.

Value addition of coir ret liquor with chemical methods
Soaking coconut husk in brackish water system for 6- 12 months is an old traditional practice carried out for the extraction of coir fibre from coconut husk. As a result of retting large quantities of organic substances including pectin, pentosan, fat, tannins, and also toxic phenols are liberated into water. All these processes contribute to pollution of water and air. This is reported to have devastating effect on the flora and fauna. This study focuses a combined chemical and biological methods should be environment friendly and economically viable treatment on ret liquor collected from various coir spinning societies.



Development of biofilm on coir based biomass carriers for treating effluent water
The golden theme of our project is to recycle the waste water effluent in a path of a sustainable way by using microbial biofilms of coir based products. There are many chemical and mechanical processes to carry over the treatment of waste water for reusing. This chemical process paves a way for an unhealthy environment. Coir is a hard and tough organic fibre which possesses high specific area and wetting ability makes use as a suitable substrate for biofilm complex aggregation of microorganisms on fixed film processes. The main attraction of the project is that, this treatment system can be easily portable to any conditions and economically viable. The research is under progression with different products.
Infrastructure facility division of polymer chemistry
NCRMI has highly sophisticated Chemical laboratory offers advanced resources for specialised chemical examination of coir pith, fibre, and associated products. These tests provide information about the quality, purity, and suitability of coir for different applications. Testing of coir and coir-related products was done in accordance with IS standards.
 Kjeldahl acid digestion
Kjeldahl acid digestion
Kjeldahl acid digestion is a commonly used method in analytical chemistry for the decomposition and digestion of organic compounds containing nitrogen. It is an essential step in the Kjeldahl method, which is employed to determine the total nitrogen content in various samples, such as coir pith, fibre, food, soil, wastewater, and biological materials.
 Automated distillation system for the estimation of nitrogen and titration system
Automated distillation system for the estimation of nitrogen and titration system
An automated distillation system for nitrogen estimation is used to separate and quantify nitrogen compounds in a sample.The entire distillation process can be automated using a dedicated instrument, which controls the heating, steam generation, condensation, and collection of the distillate. Automated titration system is used for the quantitative analysis of chemical compounds through controlled addition of a standardized solution. Automated systems often include sensors, data acquisition capabilities, and software for precise control and analysis of the results.
 Automatic fibre estimation system- for the determination of crude fibre, NDF, ADF, ADL, Cellulose, Hemicellulose. Lignin in plant materials, compound feed and food etc.
Automatic fibre estimation system- for the determination of crude fibre, NDF, ADF, ADL, Cellulose, Hemicellulose. Lignin in plant materials, compound feed and food etc.
An automatic fiber estimation system is a specialized instrument used for the determination of various fiber components in plant materials, compound feed, and food samples.Automatic fiber estimation systems offer several advantages, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and reproducibility compared to manual methods. They streamline the analysis process, reduce human error, and provide rapid and reliable results. These systems are commonly used in research and quality control laboratories in various industries, such as agriculture, animal feed production, and food processing, to assess the nutritional quality and composition of samples.
 Cold extraction system for defatting of fibre
Cold extraction system for defatting of fibre
Coir pith/ fiber may contain natural extractives, such as oils, resins, or tannins, which can impact its suitability for certain uses. Extractives analysis helps identify and quantify these substances present in the coir pith/fibre.
 pH system
pH system
The pH level of coir pith is an important parameter, especially when it is used as a growing medium. Testing the pH helps determine the acidity or alkalinity of coir pith and its potential impact on plant growth.
 Bench conductivity /TDS/Salinity/Temp. Meter
Bench conductivity /TDS/Salinity/Temp. Meter
Conductivity measurements are useful for assessing the quality and purity of coir pith, particularly in relation to its salt content or the presence of other dissolved substances.
 Flame photometer
Flame photometer
The flame photometer is primarily used for the analysis of alkali and alkaline earth metals, such as sodium (Na), potassium (K), lithium (Li), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg present in the coir pith/fibre sample).
 UV-Spectrophotometer
UV-Spectrophotometer
A UV-visible spectrophotometer is a versatile analytical instrument that can be used to determine the chemical composition of elements in coir pith/fibre. It can be employed to determine the concentration of specific compounds or functional groups that are indicative of the chemical composition of the coir pith/fibre.
 Muffle furnace and Hot air oven
Muffle furnace and Hot air oven
Muffle furnace and Hot air oven are essential tools for preparing coir pith/fibre samples for subsequent analysis, such as determining the mineral content, moisture content, or other specific components of interest. The specific temperature and duration of heating in these instruments will depend on the analysis method, desired outcomes, and the characteristics of the coir pith/fibre sample being analyzed.
 Rotary Shaker
Rotary Shaker
A rotary shaker is a laboratory instrument used for the agitation and mixing of samples in various chemical and biological applications. In the chemical analysis of coir pith/fibre,a rotary shaker can be employed for Sample Extraction, Sample Homogenization, Reagent Mixing, Sample Incubation, Extraction of Soluble Components etc.
Training of coir pith composting and house holding composting to KCCPL : A seminar on the chemical characteristics of coir pith
A seminar was conducted to provide training on coir pith composting and household composting to KCCPL. The focus of the seminar was on imparting knowledge about the chemical characteristics of coir pith, a byproduct of the coconut industry. Participants were educated on effective methods for composting coir pith, emphasizing its eco-friendly nature. The training covered key aspects of composting, including understanding the chemical composition of coir pith, optimizing conditions for microbial activity, and ensuring proper household composting practices. This initiative aimed to enhance environmental sustainability, promote waste reduction, and empower individuals at KCCPL with the skills needed for efficient and responsible composting.
Training on health and safety measures in chemical handling for coir workers of various CVCS in connection with training on frame mats to coir societies conducted by NCRMI
The training program focused on enhancing awareness and understanding of health and safety protocols associated with the handling of chemicals during the processes of bleaching and dyeing of coir fibers, specifically to produce frame mats. The sessions aimed to equip coir workers with the necessary knowledge and skills to ensure a safe working environment while maintaining the quality standards of coir products.
- Sri Abhishek C, Scientist S3
- Smt Swathy Krishna V S, Technical Officer (Polymer Chemistry)